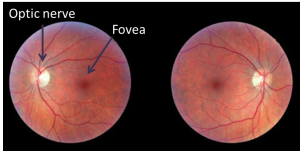
A retina scan shows the back of your eye. The retina is the part of your eye which detects light and sends the signal to your brain to work out a picture of what you can see. To do this, the retina is covered in nerves that are supplied with blood by tiny blood vessels called capillaries.
A retina scan shows you where your optic nerve and the blood vessels are and it is unique to you – even identical twins don’t have exactly the same. This pattern of capillaries will stay the same for your entire life.
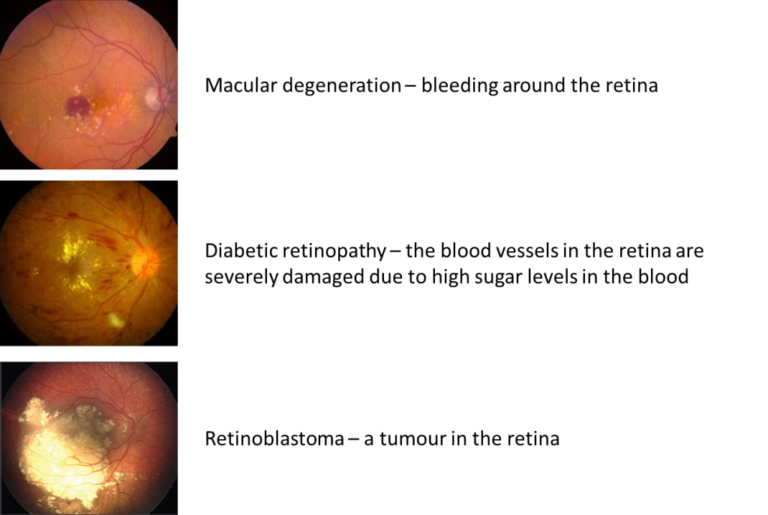
Retina scans can be used to identify people, as everyone’s is unique. They can also show symptoms of diseases such as which can change the appearance of the retina.
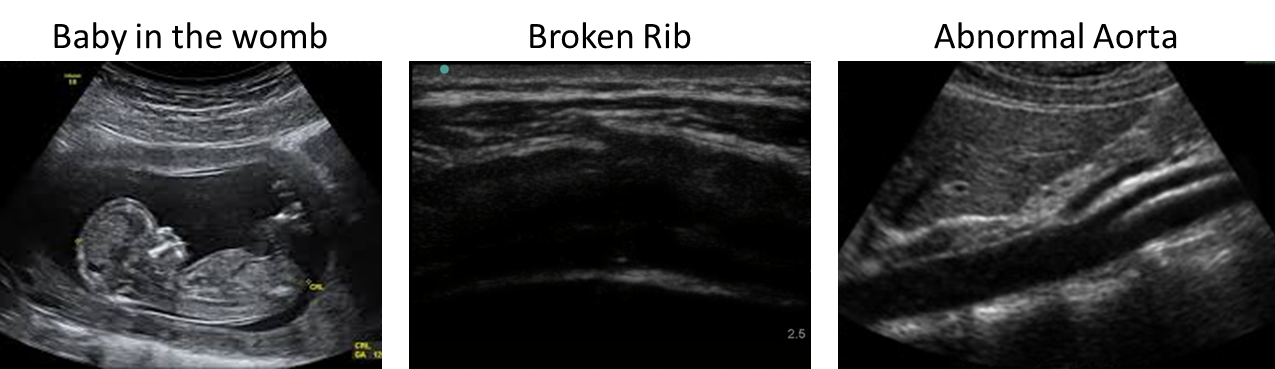
Most people have seen ultrasound scans for pregnant women, but they have lots of other uses too! They can be used to see broken bones, blood vessels, heart function, even to help doctors take biopsies properly. Ultrasound can even be used to treat soft tissue injuries.
Ultrasound works by emitting sound waves (that are too high for humans to hear), these bounce back from the tissue in your body, back to the detector and processed by a computer to determine size, shape and density of the tissue, shown real-time on a computer screen.
Infra-red vein scanners can be really helpful for doctors and nurses who are struggling to find a vein in order to take blood from a patient.
The device emits a special light called “infra-red” which is absorbed by blood differently to the surrounding tissue. This allows the device to see the where the blood vessels are and it projects an images onto the skin to show this.

Stan is a “High-fidelity patient simulator” meaning he is a full sized adult mannequin that can be programmed by a computer to have different illnesses. Simulators like Stan are used by medical students throughout the country to practice diagnosing patients.
Stan can be programmed to have different heart sounds, lung sounds and abdomen sounds. He can even talk! You can try to work out what is illnesses Stan has by using a stethoscope to listen to his organs and then treat him with different medicines.
Check out how to use a stethoscope to listen to the heart, lungs and abdomen in the “hands on health” section.
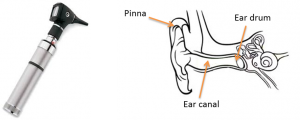
An otoscope is a medical device which you can use to look into your ears.
Otoscopes allow doctors and nurses to see the ear canal and ear drum. To do this, the pinna is pulled slightly to get better access into the ear, then the otoscope is gently place into the ear. Otoscopes have a small light on them and a magnifying glass to give a clear picture of the inside of the ear.
Otoscopes can show things like blockages, infection or broken ear drums.
An endoscopy is where the inside of your body can be viewed using an endoscope. An endoscope is a long, thin tube with a tiny camera and light at the end of it. The endoscope is linked to a computer that shows real-time images of the inside of the body.
Endoscopes can be used to look at different places in the body such as your throat, stomach and intestines. This process can be done when you are awake and doesn’t hurt but can be slightly uncomfortable.
You can use the endoscope to look at the inside of Colin the colon (lower intestine) just like a doctor would!

Keyhole surgery is where a surgeon makes tiny incisions to get inside the body in order to do surgery. This is possible because a tiny camera and light called an laparoscope is inserted and shows the surgeon on a computer the inside of the patient.
This can be used to remove organs/growths from patients or to take samples from patients to diagnose (biopsy).
Keyhole surgery leaves patients with less scarring, less blood-loss and means they don’t have to stay in hospital as long – most patients go home on the same day!
With our kits, anyone can practice using tools used in keyhole surgery without the need for a patient! Try and feed the string around the pegs or stretch an elastic band around them using the surgery tools and the camera – it’s harder than it looks!
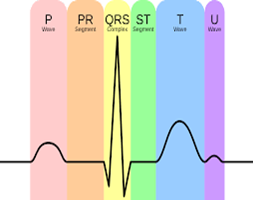
ECG stands for electrocardiogram – it measures the electrical signal of your heart!
To have an ECG, sticky tabs are placed on the skin and are attached to wires. The tabs pick up the electrical signal from the heart and this is interpreted by the computer into a trace. You have to sit completely still for this test and try not to talk! Movement can really disrupt the electrical signal.
Read below to see what each spike of your ECG means:
We inspire the next generation of medics and scientists by taking real medical and sports science equipment into schools, colleges & events all over the UK.
Company: MedicFest Ltd, trading as Medical Mavericks. Registered in England and Wales. Company Number: 12021679
© 2024 Medical Mavericks. All rights reserved.